WELCOME TO KÖNNEN
· Innovation
· Quality
· Integrity
To be an innovator and practitioner of home heating application technology in China

Staffs

Engineers
Workshop area

Heat pump manufacturing experience

Patents

Projects
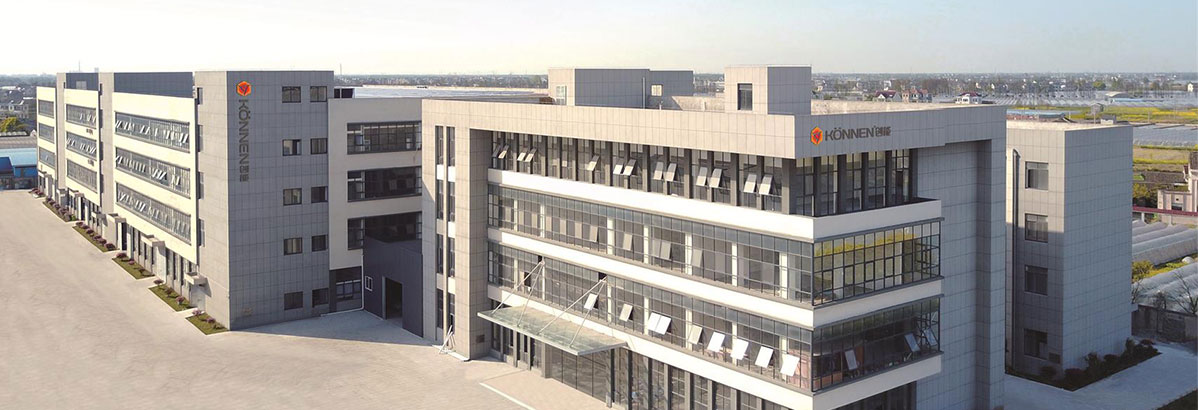
WALK TO KÖNNEN
MAIN PRODUCTS
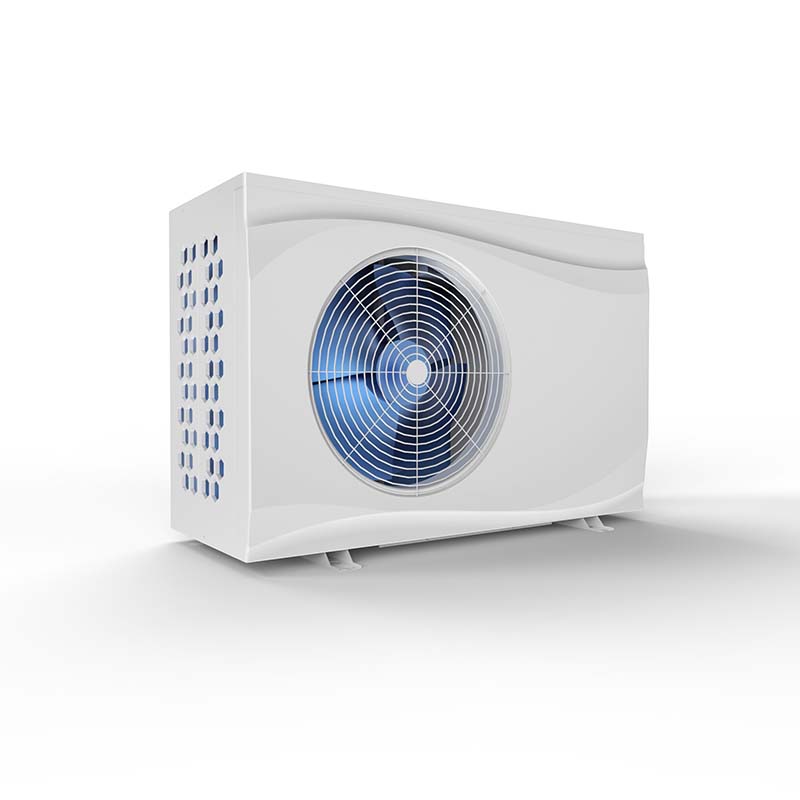

DC INVERTER SWIMMING POOL HEAT PUMP(R32)
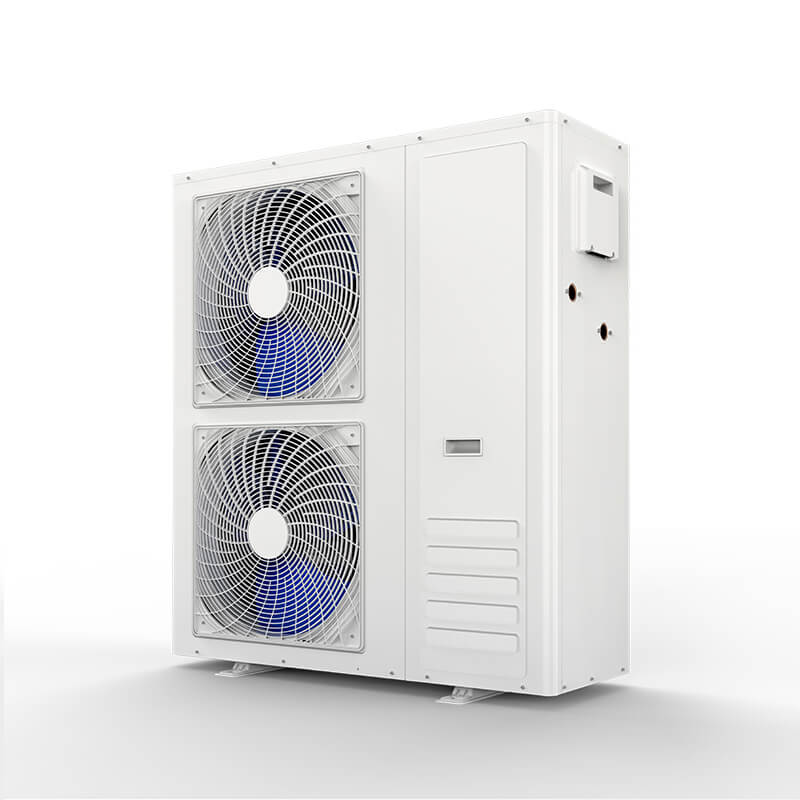

Monoblock DC Inverter air to water heat pump(R32)
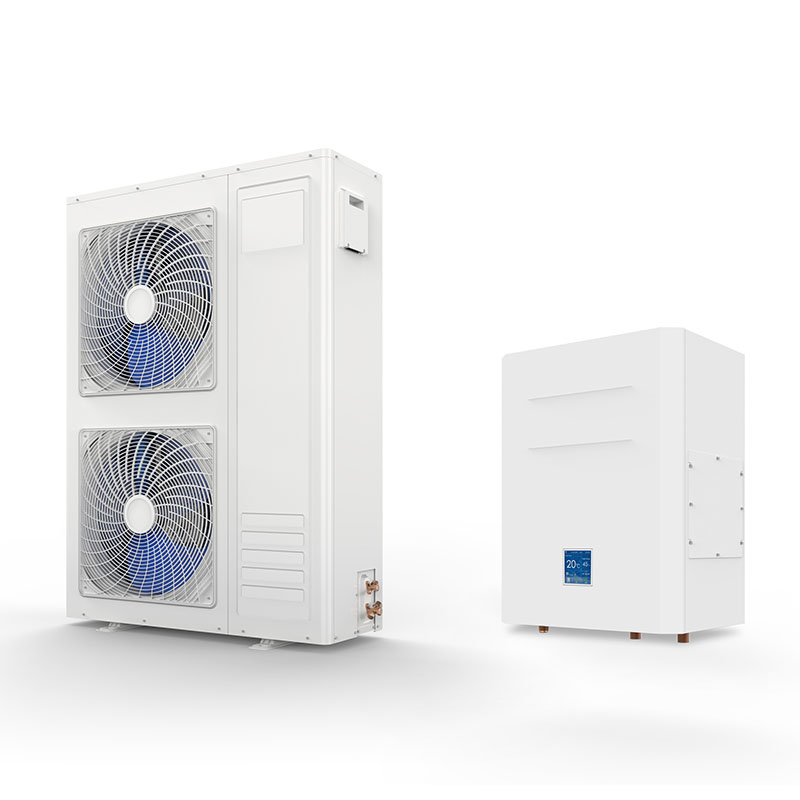

Split DC Inverter air to water heat pump(R32)

DC INVERTER SWIMMING POOL HEAT PUMP(R32)
1.Full DC Inverter technology, with DC Inverter compressor and DC brushless fan motor;
2.New R32 refrigerant, with 0 ODP and only 675 GWP.
3.High efficiency and low noise.
4.ABS plastic casing.
5.With Boost mode, Silent mode and Smart mode. Control the performance based on your requirement.

Monoblock DC Inverter air to water heat pump(R32)
1.A+++ at water temperature 35 deg C, A++ at water temperature 55 deg C.
2.R32 refrigerant.
3.With wifi function.
4.With heating + Cooling + DHW functions.
5.With “ACOL” brand expansion tank.
6."Panasonic" DC Inverter compressor.
7.DC Brushless fan motor.
8.DC Inverter "Wilo" brand circulation pump.
9."Swep" plate type heat exchanger.
10."Saginomiya" or "Sanhua" electronic expansion valve.

Split DC Inverter air to water heat pump(R32)
1.A+++ at water temperature 35 deg C, A++ at water temperature 55 deg C.
2.R32 refrigerant.
3.With wifi function.
4.With heating + Cooling + DHW functions.
5.With electric heater(3KW, 6KW, 9KW for option).
6."Panasonic" DC Inverter compressor.
7.DC Brushless fan motor.
8.DC Inverter "Wilo" brand circulation pump.
9."Swep" plate type heat exchanger.
10."Saginomiya" or "Sanhua" electronic expansion valve.
ABOUT KÖNNEN
Zhejiang CEN New Energy Stock Co., Ltd. was established in year 2001, in the early time, the company mainly produces solarwater heater controllers and other related products.In 2009,General Manager Xia Qing decided to transform the product,especially set up the heat pump department. The company began to focus on the production and sales of heat pump waterheater products, and with the establishment of the water tank production workshop in 2013,formed a research and develop-ment, production and sales system of heat pump control system, heat pump water heater and water tank.
LATEST NEWS
CONTACT US
If you have any questions about our products, you are welcome to contact us at any time
ZheJiang CEN New Energy Stock Co,.Ltd
Add:NO.468 Haicheng Road, Yucheng Town, Haiyan County, Jiaxing City, Zhejiang Province, China.
Email: aegean_heatpump@cn-xny.com.cn
TEL:+86-573-86226073